MLOps
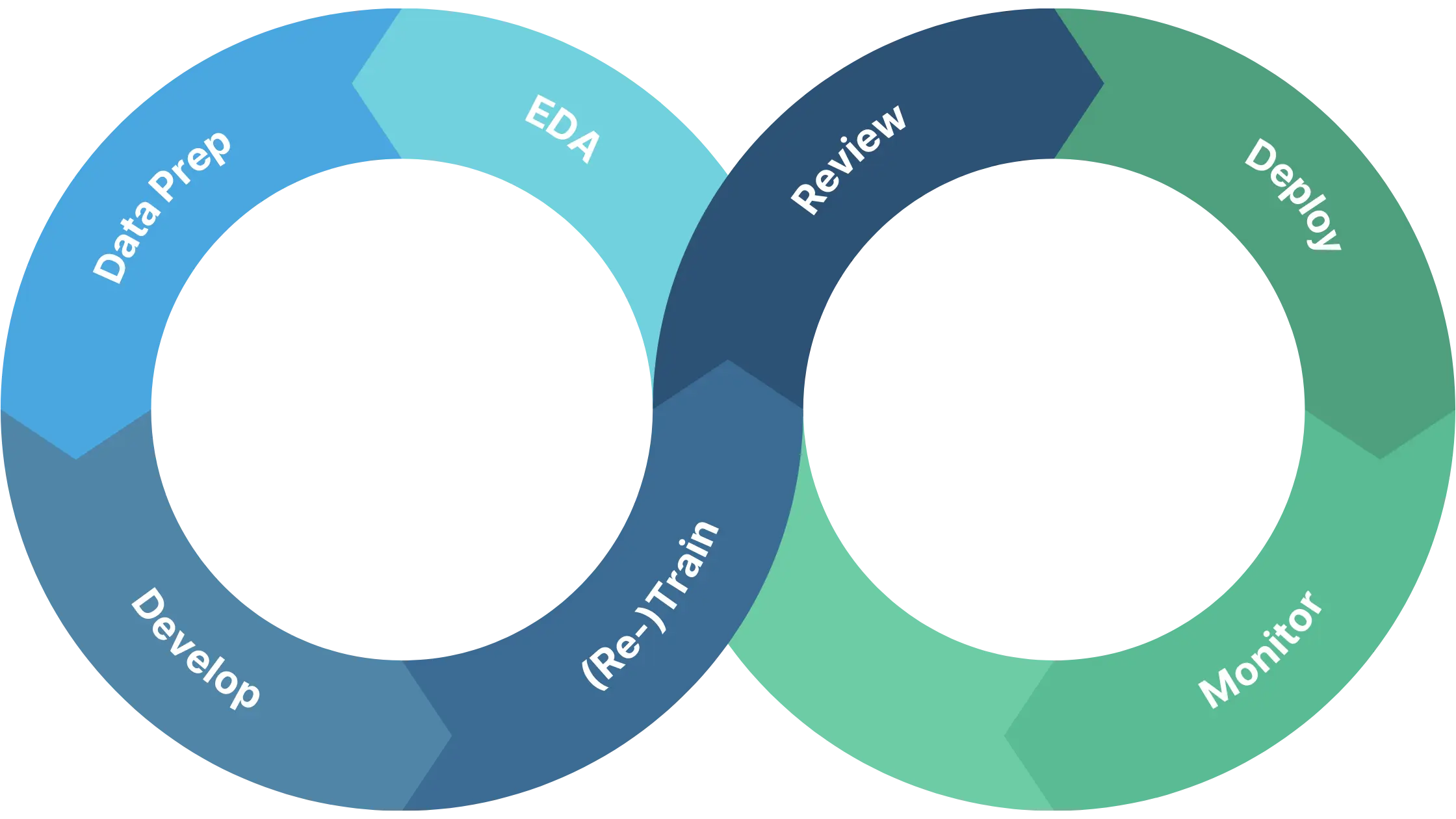
The MLOps lifecycle
The MLOps lifecycle consists of a few stages.
Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA) involves exploring and visualizing the data to gain a better understanding of its structure, distribution, and relationships between variables. During the EDA stage, data scientists and analysts use a variety of techniques to identify patterns and trends in the data, as well as to detect and correct any errors or anomalies. This might involve plotting histograms, scatterplots, or other types of visualizations, as well as performing statistical analyses and hypothesis testing. The insights gained during the EDA stage are crucial for making informed decisions about how to preprocess and transform the data prior to model training. For example, EDA might reveal the need for data cleaning, feature selection, or normalization, which can greatly impact the performance of the machine learning model.
Data Preparation involves collecting and preparing data for use in training and validating machine learning models. This involves tasks such as data cleaning, feature engineering, and data normalization.
Model development involves selecting the appropriate algorithm and optimizing its performance for a specific task. The goal of this stage is to create a machine learning model that is accurate, efficient, and scalable, and that can be deployed in a production environment. Model development typically involves several steps, including selecting an appropriate algorithm, defining the model architecture, selecting hyperparameters, and training the model on the available data. This stage often requires a significant amount of experimentation and iteration, as data scientists and engineers test and refine different approaches to achieve the best possible results.
Model training involves using the prepared data to train a machine learning model. Retraining is another important stage in the ML Ops lifecycle that involves updating an existing model with new data. Over time, the distribution of data used to train a model can change, which can lead to a decrease in performance. Retraining the model with new data can help to ensure that it remains accurate and up-to-date. Retraining typically involves using the existing model as a starting point and then training it on the new data. The parameters of the model are adjusted during training to minimize the difference between the model’s predictions and the actual outputs. Retraining can be triggered in a variety of ways, such as on a set schedule, when new data becomes available, or when the model’s performance falls below a certain threshold.
Model review involves assessing the performance of a trained machine learning model to ensure that it meets the desired criteria for accuracy, efficiency, and reliability. This stage is critical to ensuring that the model is effective and appropriate for the task at hand, and to identifying any potential issues that need to be addressed.
Model Deployment: Once the model has been evaluated and deemed ready for deployment, it is deployed to a production environment. This stage involves integrating the model into the existing infrastructure and ensuring that it is scalable and reliable.
Model Monitoring and Maintenance: After the model has been deployed, it is important to monitor its performance in production and make any necessary adjustments. This includes monitoring for changes in data distribution, retraining the model if necessary, and addressing any bugs or issues that arise.
Saturn Cloud
Saturn cloud workspaces: Saturn cloud workspaces are scalable development environments that can connect to an associated dask cluster. This gives the data scientist access to tremendous amount of computing power, RAM, and GPUs. This workspace is commonly used for EDA, Data Preparation as well as Model Development
Saturn cloud jobs: Saturn cloud jobs have the exact same specifications and configuration as Saturn Cloud workspaces, and can also connect to an associated Dask cluster. These jobs can be triggered via an API, or on a schedule. These are often used for Model (Re-)Training
Saturn cloud deployments: Saturn cloud deployments can deploy any user code that serves HTTP traffic on port 8000. This is commonly used for Model Deployment, however you can also leverage other MLOps providers for tighter integration with a Model registry.
Integrations
Saturn Cloud integrates with a variety of MLOps providers for model deployment, model registry, experiment tracking, and model monitoring.
These include, but are not limited to:
- Comet
- Weights and Biases
- Verta.ai
- Neptune.ai
Often times, you can connect to these cloud services directly. If you require these tools to be deployed within your AWS account, we can manage this for you as a custom integration, within the Saturn Cloud Kubernetes cluster.
