Deploying Jobs
A Saturn Cloud job is a resource that runs automated tasks on a schedule or can be triggered manually. Jobs are commonly used to schedule training pipelines and ETL jobs.
When to Use Jobs
Jobs are best used for:
- Training pipelines that run overnight or on a schedule
- ETL jobs that process data regularly
- Model retraining workflows
- Data processing tasks that don’t need interactive development
- Cron jobs for regular maintenance tasks
When to Use Interactive Resources Instead
Use Jupyter Servers or R Servers for:
- Exploratory data analysis
- Interactive development and prototyping
- Real-time collaboration
- Debugging and troubleshooting
Getting Started with Jobs
The recommended approach is to develop your code interactively first, then convert it to a job once it works reliably:
- Develop interactively: Use a Jupyter Server or R Server to develop and test your code
- Convert to a job: Once your code works reliably, clone it as a job (see “Convert the interactive environment into a job” below)
- Set up scheduling: Configure when and how often your job should run using Dispatching Jobs for Research Workflows
This article covers the patterns that will help you work faster with these resources. This approach is similar to developing dashboards, models and apis.
Related Articles
- Dispatching Jobs for Research Workflows: Learn how to schedule jobs and dispatch them programmatically for research workflows
- Massively Parallel Jobs for Research Workflows: Scale your jobs to run across hundreds or thousands of resources for parallel execution
Develop Interactively
The iteration cycle for deploying code is slow. Every time you start one of these resources, we need to allocate a machine, download your docker image, run any initialization scripts you have before we actually get to executing your code. You should be extremely confident that the when you start your resource, it will work.
Part of this means you should run your code in the exact same environment you are going to deploy it in. The fact that it runs fine on your laptop, does not mean it will run fine when you deploy it, because you have different files and libraries on your laptop compared to what you will be running in the cloud.
We recommend running jobs in a Jupyter or RStudio server, either via the web terminal or through SSH. If you are planning on deploying a notebook, Papermill can be run in the terminal as well.
Keep track of software dependencies
If you have manually installed any packages (either pip, conda, or cran) in your development environment, those will be missing from your deployment. It’s a good idea to edit the resource, and drop the package into the extra packages section each time you install a package, so that it will be installed at startup the next time you restart your resource. This will also ensure that any deployments you create from this workspace will also pick up the exact same dependencies.
Make sure everything is in Git
When a job is executed, all source code is cloned from a Git repository. Nothing is synced from your workspace to the deployment. If a file isn’t present in Git, it won’t end up on your deployment. Make sure that all source code is committed to your Git repository
Be careful loading data files from disk
If you are working with data files, you can usually work with them without downloading them to disk using boto3 or other libraries. If you do have to download them to disk - just know that these data files won’t automatically be present in any deployments. You can modify your start script to download the files at startup, or modify your deployment to download the file when it needs to access them.
Working directory
Don’t change into another directory when you run your command. The job will be run out of the same directory you are in. If you do want to run the command out of a different directory, set that path as the “working directory” of your resource.
Convert the interactive environment into a job
After you are happy with your dashboard, model or API running in the terminal, it should be easy to deploy that. Click on the Manage tab, and click “Clone as a Job”.
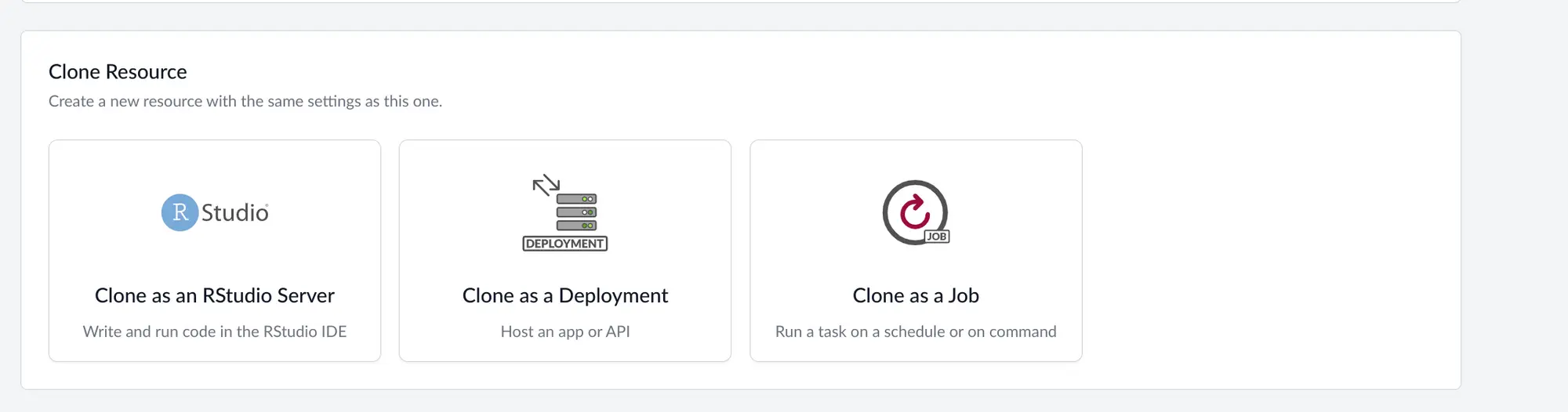
Saturn Cloud will ask you for the command you use to run your deployment. That command should be exactly what you ran inside your interactive environment.
Jobs should be managed by a group
Once you have a deployment or job running - you should transfer it over to a group. The reason you would want to do that is to ensure that if you go on vacation or get sick, that other people on your team can manage the job.
Groups can only be created by Saturn Cloud admins - so before doing this, make sure a Saturn Cloud admin for your installation creates a group.
The way to transfer ownership to the group, is to clone the resource. When you clone the deployment, you will be able to select a new owner (in this case, select the group that you are in).
Ensure that the group has all the necessary secrets
If you created a job as your Saturn Cloud user, it probably has your secrets attached. Group owned resources can only access secrets that are accessible to the group. You will have to click on the “secrets” tab, and make sure equivalent secrets are available for the group.
Ensure that the group has all the git access
As mentioned - deployments get their source code from the git integration. Once you clone the job into a group owned resource, you will need to ensure that the group has SSH keys with sufficient privileges to clone the necessary git repositories.
Reproducibility
Build Docker images
If you are installing packages at startup, either using extra packages, or by customizing a start script, it is a good idea to build an image. You can use the Saturn Cloud image builder to make a new version of your image with all the dependencies that are being installed at startup. This ensures that your software dependencies will never change over time. If you are installing packages at startup, and new versions of packages are released, you can accidentally pick up those versions.
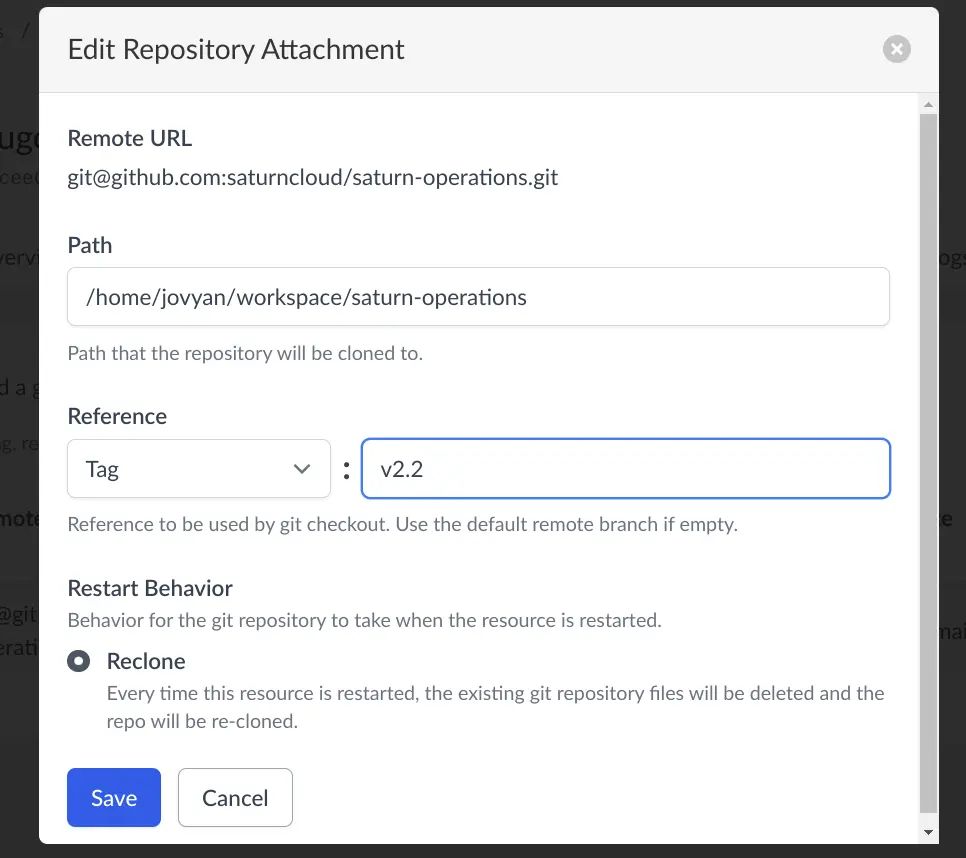
Use git tags
If the source code for your deployment or job is being actively developed, it is a good idea to deploy from a tag. This will ensure that as you or your team continue to work on the code base, no changes will impact your application that accidentally change it’s behavior. To change to a tag - click on the “Git Repositories” tag. Edit the repository, and type in the tag that you want to use.